User Manual for Release 6.0
Oracle VM VirtualBox Base Packages - 6.1.26. Freely available for Windows, Mac OS X, Linux and Solaris x86 platforms under GPLv2: Platform. Windows Installer. Solaris 10 5/08 and later or Solaris 11. To explicitly extract the Windows Guest Additions for another platform than the current running one, such as 64-bit files on a 32-bit system, you must use the appropriate platform installer. Use VBoxWindowsAdditions-x86.exe or VBoxWindowsAdditions-amd64.exe with the /extract parameter. Oracle VM VirtualBox Base Packages - 6.1.26. Freely available for Windows, Mac OS X, Linux and Solaris x86 platforms under GPLv2: Platform. Windows Installer. Solaris 10 5/08 and later or Solaris 11.
E97727-03
For further details, refer to the 'Virtual networking' chapter of the Oracle VM VirtualBox User Manual. Attaching Virtual Media to a VM. Like a real computer, your VM needs a storage device, such as a hard disk, to boot from and for storing and retrieving system and user data. So, let's now create a virtual hard disk for the VM. Oracle VM VirtualBox R User Manual Version 4.2.12 c 2004-2013 Oracle Corporation http://www.virtualbox.org. It should be possible to use Oracle VM VirtualBox on most systems based on Linux kernel 2.6 or 3.x using either the Oracle VM VirtualBox installer or by doing a manual installation. See Section 2.3, “Installing on Linux Hosts”. However, the formally tested and supported Linux distributions are those for which we offer a dedicated package. Oracle VM VirtualBox R User Manual Version 4.1.18 c 2004-2012 Oracle Corporation http://www.virtualbox.org.
Oracle Vm Virtualbox Manager Download
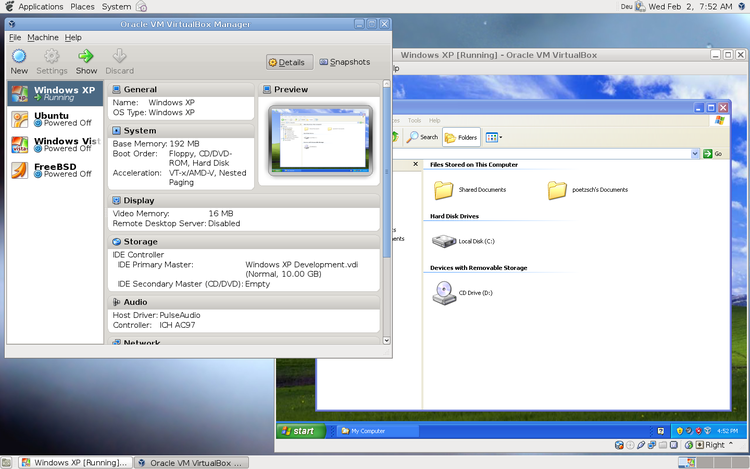
Run Windows 7 in a Virtual Machine under Windows 10. I use Oracle VirtualBox to run XP Pro, Windows 7 Pro and even a copy of OS/2 Warp 4 as VMs via Oracle VirtualBox. I can have any or all of them running at the same time on my Windows 10 Desktop along with whatever I want running natively on Windows 10. See here: Oracle VirtualBox. Now if the host was 32-bit that might be causing it, but the OP said Win-Ult-64. I guess it could be the Windows build though, since I have not build a Windows host for a while. The only differences are when selecting 64 VBox enables io-apic and sets a few other defaults.
Table of Contents
- Preface
- 1 Audience
- 2 Related Documents
- 3 Conventions
- 4 Documentation Accessibility
- 5 Access to Oracle Support
- 1 First Steps
- 1.1 Why is Virtualization Useful?
- 1.2 Some Terminology
- 1.3 Features Overview
- 1.4 Supported Host Operating Systems
- 1.5 Host CPU Requirements
- 1.6 Installing Oracle VM VirtualBox and Extension Packs
- 1.7 Starting Oracle VM VirtualBox
- 1.8 Creating Your First Virtual Machine
- 1.9 Running Your Virtual Machine
- 1.9.1 Starting a New VM for the First Time
- 1.9.2 Capturing and Releasing Keyboard and Mouse
- 1.9.3 Typing Special Characters
- 1.9.4 Changing Removable Media
- 1.9.5 Resizing the Machine's Window
- 1.9.6 Saving the State of the Machine
- 1.10 Using VM Groups
- 1.11 Snapshots
- 1.11.1 Taking, Restoring, and Deleting Snapshots
- 1.11.2 Snapshot Contents
- 1.12 Virtual Machine Configuration
- 1.13 Removing and Moving Virtual Machines
- 1.14 Cloning Virtual Machines
- 1.15 Importing and Exporting Virtual Machines
- 1.15.1 About the OVF Format
- 1.15.2 Importing an Appliance in OVF Format
- 1.15.3 Exporting an Appliance in OVF Format
- 1.15.4 Exporting an Appliance to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- 1.15.5 The Cloud Profile Manager
- 1.16 Global Settings
- 1.17 Alternative Front-Ends
- 2 Installation Details
- 2.1 Installing on Windows Hosts
- 2.1.1 Prerequisites
- 2.1.2 Performing the Installation
- 2.1.3 Uninstallation
- 2.1.4 Unattended Installation
- 2.1.5 Public Properties
- 2.2 Installing on Mac OS X Hosts
- 2.2.1 Performing the Installation
- 2.2.2 Uninstallation
- 2.2.3 Unattended Installation
- 2.3 Installing on Linux Hosts
- 2.3.1 Prerequisites
- 2.3.2 The Oracle VM VirtualBox Kernel Modules
- 2.3.3 Performing the Installation
- 2.3.4 The vboxusers Group
- 2.3.5 Starting Oracle VM VirtualBox on Linux
- 2.4 Installing on Oracle Solaris Hosts
- 2.4.1 Performing the Installation
- 2.4.2 The vboxuser Group
- 2.4.3 Starting Oracle VM VirtualBox on Oracle Solaris
- 2.4.4 Uninstallation
- 2.4.5 Unattended Installation
- 2.4.6 Configuring a Zone for Running Oracle VM VirtualBox
- 3 Configuring Virtual Machines
- 3.1 Supported Guest Operating Systems
- 3.1.1 Mac OS X Guests
- 3.1.2 64-bit Guests
- 3.2 Unattended Guest Installation
- 3.2.1 An Example of Unattended Guest Installation
- 3.3 Emulated Hardware
- 3.4 General Settings
- 3.4.1 Basic Tab
- 3.4.2 Advanced Tab
- 3.4.3 Description Tab
- 3.4.4 Disk Encryption Tab
- 3.5 System Settings
- 3.5.1 Motherboard Tab
- 3.5.2 Processor Tab
- 3.5.3 Acceleration Tab
- 3.6 Display Settings
- 3.6.1 Screen Tab
- 3.6.2 Remote Display Tab
- 3.6.3 Recording Tab
- 3.7 Storage Settings
- 3.8 Audio Settings
- 3.9 Network Settings
- 3.10 Serial Ports
- 3.11 USB Support
- 3.11.1 USB Settings
- 3.11.2 Implementation Notes for Windows and Linux Hosts
- 3.12 Shared Folders
- 3.13 User Interface
- 3.14 Alternative Firmware (EFI)
- 3.14.1 Video Modes in EFI
- 3.14.2 Specifying Boot Arguments
- 4 Guest Additions
- 4.1 Introduction to Guest Additions
- 4.2 Installing and Maintaining Guest Additions
- 4.2.1 Guest Additions for Windows
- 4.2.2 Guest Additions for Linux
- 4.2.3 Guest Additions for Oracle Solaris
- 4.2.4 Guest Additions for OS/2
- 4.3 Shared Folders
- 4.3.1 Manual Mounting
- 4.3.2 Automatic Mounting
- 4.4 Drag and Drop
- 4.4.1 Supported Formats
- 4.4.2 Known Limitations
- 4.5 Hardware-Accelerated Graphics
- 4.5.1 Hardware 3D Acceleration (OpenGL and Direct3D 8/9)
- 4.5.2 Hardware 2D Video Acceleration for Windows Guests
- 4.6 Seamless Windows
- 4.7 Guest Properties
- 4.7.1 Using Guest Properties to Wait on VM Events
- 4.8 Guest Control File Manager
- 4.8.1 Using the Guest Control File Manager
- 4.9 Guest Control of Applications
- 4.10 Memory Overcommitment
- 4.10.1 Memory Ballooning
- 4.10.2 Page Fusion
- 5 Virtual Storage
- 5.1 Hard Disk Controllers: IDE, SATA (AHCI), SCSI, SAS, USB MSD, NVMe
- 5.2 Disk Image Files (VDI, VMDK, VHD, HDD)
- 5.3 The Virtual Media Manager
- 5.4 Special Image Write Modes
- 5.5 Differencing Images
- 5.6 Cloning Disk Images
- 5.7 Host Input/Output Caching
- 5.8 Limiting Bandwidth for Disk Images
- 5.9 CD/DVD Support
- 5.10 iSCSI Servers
- 5.11 vboximg-mount: A Utility for FUSE Mounting a Virtual Disk Image
- 5.11.1 Viewing Detailed Information About a Virtual Disk Image
- 5.11.2 Mounting a Virtual Disk Image
- 6 Virtual Networking
- 6.1 Virtual Networking Hardware
- 6.2 Introduction to Networking Modes
- 6.3 Network Address Translation (NAT)
- 6.3.1 Configuring Port Forwarding with NAT
- 6.3.2 PXE Booting with NAT
- 6.3.3 NAT Limitations
- 6.4 Network Address Translation Service
- 6.5 Bridged Networking
- 6.6 Internal Networking
- 6.7 Host-Only Networking
- 6.8 UDP Tunnel Networking
- 6.9 VDE Networking
- 6.10 Limiting Bandwidth for Network Input/Output
- 6.11 Improving Network Performance
- 7 VBoxManage
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Commands Overview
- 7.3 General Options
- 7.4 VBoxManage list
- 7.5 VBoxManage showvminfo
- 7.6 VBoxManage registervm/unregistervm
- 7.7 VBoxManage createvm
- 7.8 VBoxManage modifyvm
- 7.8.1 General Settings
- 7.8.2 Networking Settings
- 7.8.3 Miscellaneous Settings
- 7.8.4 Recording Settings
- 7.8.5 Remote Machine Settings
- 7.8.6 Teleporting Settings
- 7.8.7 Debugging Settings
- 7.8.8 USB Card Reader Settings
- 7.8.9 Autostarting VMs During Host System Boot
- 7.9 VBoxManage clonevm
- 7.10 VBoxManage movevm
- 7.11 VBoxManage import
- 7.12 VBoxManage export
- 7.12.1 Export to OVF
- 7.12.2 Export to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
- 7.13 VBoxManage startvm
- 7.14 VBoxManage controlvm
- 7.15 VBoxManage discardstate
- 7.16 VBoxManage adoptstate
- 7.17 VBoxManage snapshot
- 7.18 VBoxManage closemedium
- 7.19 VBoxManage storageattach
- 7.20 VBoxManage storagectl
- 7.21 VBoxManage bandwidthctl
- 7.22 VBoxManage showmediuminfo
- 7.23 VBoxManage createmedium
- 7.24 VBoxManage modifymedium
- 7.25 VBoxManage clonemedium
- 7.26 VBoxManage mediumproperty
- 7.27 VBoxManage encryptmedium
- 7.28 VBoxManage checkmediumpwd
- 7.29 VBoxManage convertfromraw
- 7.30 VBoxManage getextradata/setextradata
- 7.31 VBoxManage setproperty
- 7.32 VBoxManage usbfilter add/modify/remove
- 7.33 VBoxManage sharedfolder add/remove
- 7.34 VBoxManage guestproperty
- 7.35 VBoxManage guestcontrol
- 7.36 VBoxManage metrics
- 7.37 VBoxManage natnetwork
- 7.38 VBoxManage hostonlyif
- 7.39 VBoxManage dhcpserver
- 7.40 VBoxManage usbdevsource
- 7.41 VBoxManage mediumio
- 7.41.1 Synopsis
- 7.41.2 Description
- 7.42 VBoxManage debugvm
- 7.42.1 Synopsis
- 7.42.2 Description
- 7.43 VBoxManage extpack
- 7.43.1 Synopsis
- 7.43.2 Description
- 7.43.3 Examples
- 7.44 VBoxManage unattended
- 7.44.1 Synopsis
- 7.44.2 Description
- Glossary
Virtualbox User Guide
Oracle Vm Virtualbox Windows 7
Copyright © 2004, 2019 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Legal Notices
Currently, Oracle VM VirtualBox runs on the following host OSes:
Oracle Virtualbox 32 Bit Windows 7 Free
Oracle Vm Virtualbox User Manual Rus 1
Windows hosts (64-bit):
Windows 7
Windows 8
Windows 8.1
Windows 10 RTM (1507) build 10240
Windows 10 November Update (1511) build 10586
Windows 10 Anniversary Update (1607) build 14393
Windows 10 Creators Update (1703) build 15063
Windows 10 Fall Creators Update (1709) build 16299
Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803) build 17134
Windows 10 October 2018 Update (1809) build 17763
Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2019
Mac OS X hosts (64-bit):
10.12 (Sierra)
10.13 (High Sierra)
10.14 (Mojave)
Intel hardware is required. See also Known Limitations.
Linux hosts (64-bit). Includes the following:
Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, 18.04 LTS and 18.10
Debian GNU/Linux 9 ('Stretch')
Oracle Linux 6 and 7
Redhat Enterprise Linux 6 and 7
Fedora 28 and 29
Gentoo Linux
SUSE Linux Enterprise server 12 and 15
openSUSE Leap 42.3 and 15.0
It should be possible to use Oracle VM VirtualBox on most systems based on Linux kernel 2.6 or 3.x using either the Oracle VM VirtualBox installer or by doing a manual installation. See Section 2.3, “Installing on Linux Hosts”. However, the formally tested and supported Linux distributions are those for which we offer a dedicated package.
Note that Linux 2.4-based host OSes are no longer supported.
Oracle Solaris hosts (64-bit only). The following versions are supported with the restrictions listed in Known Limitations:

Note that the above list is informal. Oracle support for customers who have a support contract is limited to a subset of the listed host OSes. Also, any feature which is marked as experimental is not supported. Feedback and suggestions about such features are welcome.
Virtualbox 32 Bit Windows 7
User Manual Pdf
Virtualbox 32 Bit Version
Copyright © 2004, 2019 Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Legal Notices